Known as far back as June 2022, the Play (or PlayCrypt) ransomware is a leading malicious actor spreading terror across the digital landscape.
The Play ransomware group has established itself as one of the most threatening and formidable, affecting a wide range of businesses and critical infrastructures in North America, South America, Europe and Australia, with over 787 victims recorded to date.
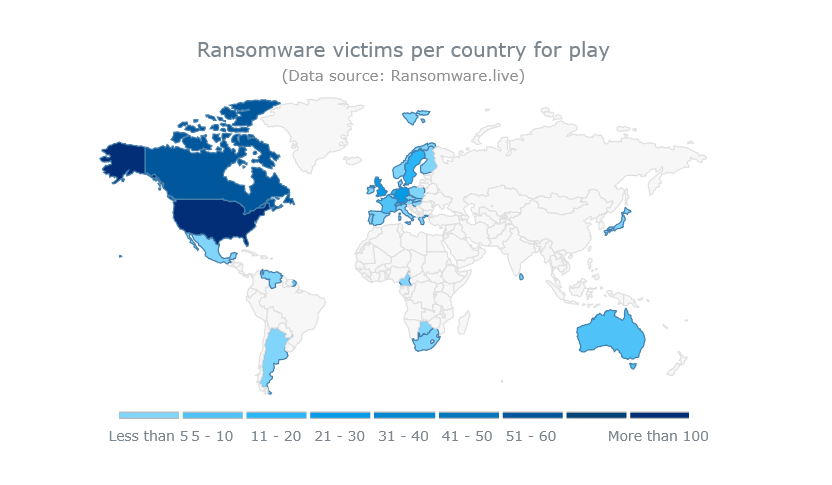
According to Ransomfeed, the group has already claimed no fewer than 47 victims in the last month of February 2025.
Behind this almost playful name lies a much darker reality for victimized companies and institutions.
Play has again distinguished itself by its dual extortion techniques (exfiltration and intermittent encryption of data, encrypting only certain parts of files), its use ofcustomized tools and its targeting of various sectors around the world.
Recently, links have been established between Play and North Korean state actors (Jumpy Pisces), increasing the seriousness of this threat. See the article: When Pyongyang’s hackers turn to ransomware, on LeMagIt…
Table des matières
ToggleA sophisticated and devastating attack strategy
Here’s an overview of the tactics, techniques and procedures (TTP) used by the Play ransomware:
- Initial access: the Play group gains initial access to target networks via valid accounts.
- Exploitation of vulnerabilities in publicly available applications, in particular known vulnerabilities in FortiOS (CVE-2018-13379 and CVE-2020-12812) and Microsoft Exchange (ProxyNotShell [CVE-2022-41040 and CVE-2022-41082]). Use of external services such as Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and Virtual Private Networks (VPN) for initial access.
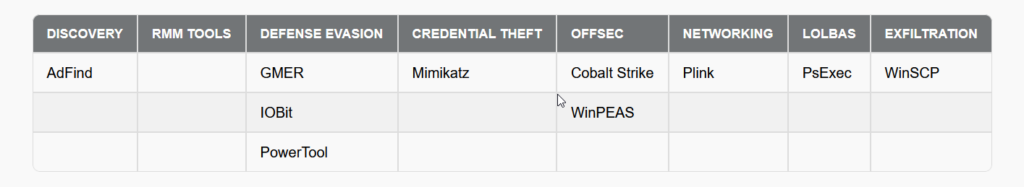
- Lateral movement and execution: the Play ransomware actors use command and control (C2) applications, including Cobalt Strike and SystemBC, as well as tools such as PsExec, to facilitate lateral movement and file execution.
- Once established on a network, ransomware actors look for unsecured credentials. Use of Mimikatz to gain domain administrator access.
- Use of Windows Privilege Escalation Awesome Scripts (WinPEAS) to search for other privilege elevation paths.
- Distribution of executables via Group Policy Objects.
- Exfiltration and encryption: ransomware operators often divide compromised data into segments and use tools such as WinRAR to compress files in .RAR format for exfiltration.
- Use of WinSCP to transfer data from a compromised network to accounts controlled by the actor.
- Encryption of files with hybrid AES-RSA encryption using intermittent encryption, encrypting all file portions of 0x100000 bytes.
- A .play extension is added to file names, and a ransom note entitled ReadMe[.]txt is placed in the file directory.
- Backup destruction: Play attacks backup systems to deprive victims of alternative data recovery options, employing meticulous strategies to eliminate backup capabilities.
The Impact of attacks on organizations victimized by Play ransomware
The Play ransomware group uses a double extortion model, encrypting systems after exfiltrating data.
The ransom note instructs victims to contact the Play ransomware group at an email address ending in @gmx[.]de.
Ransom payments are made in cryptocurrency to wallet addresses provided by Play actors. If a victim refuses to pay the requested ransom, the ransomware actors threaten to publish the exfiltrated data on their leak site on the Tor network (URL [. ]onion).
- The targeted sectors are varied: telecommunications, healthcare, media, transport, construction and government. Managed Service Providers are also targeted.
- Regions: attacks have been observed in North America, South America, Europe and Australia.
Linux variant and ESXi targeting
A new Linux variant of the Play ransomware has been discovered, specifically targeting VMware ESXi environments. This discovery suggests an expansion of Play attacks to the Linux platform.
Example of a Play ransomware attack
The Play ransomware group has, for example, claimed responsibility for a cyberattack that disrupted Krispy Kreme‘s operations in November 2024. The incident resulted in disruptions to the company’s online ordering system in the USA. Krispy Kreme detected unauthorized activity on some of its IT systems on November 29 and took steps to contain and remediate the breach, hiring external cybersecurity experts to investigate the impact of the attack.
Play Group claimed to have collected and stolen files containing private and personal confidential data, customer documents, budgets, payslips, accounting data, contracts, taxes, IDs and financial information.
The group then, of course, threatened to publish the data unless a ransom was paid…

How to protect yourself against the Play ransomware? A multi-layered approach is essential
To deal with the Play ransomware, you need a proactive, multi-layered defense strategy. This approach can make all the difference in keeping you safe.
Here are some essential measures to put in place today:
Access management is always your first line of defense.
Implement multi-factor authentication on all your critical services.
Adopt the recommendations of the NIST CyberFramework, for example, notably for your password policies, by favoring long passphrases (minimum 16 characters).
Configure your access controls according to the principle of least privilege, and consider JIT (just-in-time) access for administrator accounts.
Systematic maintenance of your infrastructure is also a must for your security:
apply security patches promptly, especially for known vulnerabilities on systems exposed to the Internet. Keep your antivirus software up to date, with real-time detection enabled. Segment your networks to limit potential propagation, and disable unused ports.
Finally, your backup strategy must be impeccable. Keep several copies of your critical data in a physically separate, secure location. Make sure these backups are encrypted and immutable (impossible for attackers to modify). Regularly test your restoration procedures.
Crisis management: what to do in the event of an attack
If, despite all your precautions, you fall victim to a Play attack, immediate action is crucial. Immediately isolate infected systems to contain the spread of the virus. Report the incident to the appropriate authorities, such as the FBI, CISA or, in France, ANSSI.
Let’s stress a key point: cybersecurity experts, including the FBI, strongly advise against paying ransom. Not only does it fund criminal organizations, but there is no guarantee that your data will be recovered. Instead, call in incident response specialists and be prepared to restore from your backups.
The Play ransomware represents the evolution of a sophisticated cybercriminal threat that is likely to continue to target organizations heavily into 2025.
Vigilance, preparation and a defense-in-depth strategy remain your best assets in the face of this persistent threat. Don’t wait until you’re a victim to take action – prevention remains your most cost-effective cybersecurity investment.
FAQ
How can I detect an infection by the Play ransomware?
– Presence of encrypted files with the “.play” extension.
– Discovery of a ransom note named “ReadMe.txt.”
– Unusual network activity, particularly outbound connections to suspicious IP addresses.
– Use of tools such as Mimikatz, PsExec, WinRAR, or WinSCP.
– Security setting modifications, such as the deactivation of antivirus software.
– Presence of malware such as SystemBC and DTrack.
What preventive measures can I take to protect against the Play ransomware?
– Implement a strong password policy: Use long, complex passwords stored securely.
– Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): Especially for webmail, VPNs, and administrative accounts.
– Regularly update systems: Quickly patch known vulnerabilities in operating systems, software, and firmware, particularly those exposed to the internet.
– Segment the network: To limit ransomware propagation in case of infection.
– Deploy an Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solution: To detect and block suspicious activities.
– Filter network traffic: To prevent unauthorized connections to internal services.
– Install and maintain up-to-date antivirus software: On all workstations and servers.
– Regularly audit user accounts: Particularly privileged accounts, and enforce the principle of least privilege.
– Disable unused ports: To reduce the attack surface.
– Maintain offline backups of data: Ensuring they are encrypted and immutable.
What should I do if I fall victim to a Play ransomware attack?
– Immediately isolate infected systems: To prevent further spread.
– Report the incident to the relevant authorities: Such as the FBI, CISA, ANSSI, etc.
– Do not pay the ransom: There is no guarantee of data recovery, and it encourages criminal activity.
– Restore data from backups: Ensuring backups are recent and free from infection.
– Analyze the incident: To identify the attack’s cause and strengthen security measures.
– Consult an incident response specialist: For professional assistance and customized solutions.
