The cyberthreat landscape continues to evolve, with malicious actors becoming ever more determined and organized.
Among these groups, the Qilin ransomware has emerged as one of the most worrying threats of 2025, targeting organizations worldwide and wreaking considerable havoc.
If you’re looking for detailed information on this emerging cyberthreat and how to protect your organization, this article will provide you with an in-depth analysis of the Qilin ransomware and the solutions SOS Ransomware can provide in the event of an attack.
Table des matières
ToggleWhat is the Qilin ransomware?
The Qilin ransomware (also known asAgenda) is a malware program that appeared in July 2022 and operates on a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model.
This model allows developers to make their malware available to affiliates in exchange for a share of the profits generated by attacks.
The name “Qilin” refers to a Chinese mythological creature combining dragon and horned animal characteristics, sometimes compared to a unicorn. However, despite this reference to Chinese mythology, the group behind this ransomware is more likely to be linked to Russian-speaking cybercriminals.

Qilin stands out in particular for its highly customizable modular design…
Indeed, affiliates can fine-tune the parameters of each attack to suit their specific targets.
In particular, they can determine the optimal encryption mode for the situation, whether fast encryption to maximize immediate impact, or more selective encryption to avoid detection.
This flexibility also extends to the choice of file extensions to be added after encryption, enabling a unique signature to be created for each attack campaign. Malware can also be configured to ignore certain strategic files or directories, ensuring that the operating system remains functional.
Finally, affiliates can define which processes and services should be stopped before the attack to bypass security defenses and optimize encryption efficiency.
Qilin’s evolution since its emergence
Since its emergence in 2022, the Qilin ransomware has undergone a significant evolution both in technical terms and in the scale of its activity:
- July 2022: First sighting by Trend Micro under the name “Agenda”, with code written in Go language (Golang).
- October 2022: First victim listed on the Qilin dark web leak site.
- December 2022: Complete redesign of the ransomware in Rust language, improving its portability and capabilities.
- March 2023: Group-IB infiltrates the group and reveals that affiliates receive between 80% and 85% of ransom payments.
- Late 2023: Activity peaks with the deployment of one of the most advanced Linux encryptors, specifically targeting VMware ESXi virtual machines.
- Early 2025: Attacks intensify, with over 310 victims claimed to date.
- March 2025: Microsoft reveals that a group of North Korean hackers, Moonstone Sleet, is now using the Qilin ransomware in some of their attacks.
This constant evolution testifies to Qilin’s adaptability and determination to remain a leading threat in the cyberattack landscape.
Operation and attack methods
Qilin ransomware employs sophisticated tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) that generally follow a well-honed attack pattern.
1. Initial access
To infiltrate their victims’ systems, Qilin affiliates deploy an arsenal of diversified intrusion techniques. Their phishing campaigns are meticulously crafted, with convincing emails containing booby-trapped attachments or links to compromised sites.
Attackers are also opportunistic in exploiting technical vulnerabilities, focusing particularly on flaws in software exposed on the Internet.
The CVE-2023-27532 vulnerability in Veeam Backup & Replication represents one of their favorite targets, as do inadequately secured Fortinet devices. Remote access services such as RDP are also a preferred vector, especially when not protected by multi-factor authentication.
Finally, attackers do not hesitate to use stolen legitimate credentials to bypass traditional defense mechanisms.
2. Lateral movement and elevation of privileges
Once initial access has been gained, attackers :
- use Mimikatz to extract credentials and gain administrator privileges
- Use PsExec to move laterally in the network
- Run tools such as Cobalt Strike to deploy the malicious payload
- Manipulate access tokens to elevate privileges to SYSTEM level
- etc
3. Data exfiltration
Even before encryption, Qilin’s operators implement a methodical exfiltration strategy for sensitive data. This step enables them to exert double pressure on their victims. The attackers begin by identifying the most valuable information – confidential documents, personal data, intellectual property – which they then transfer to their own servers.
To optimize this process, they use compression tools, reducing the volume of data and minimizing the risk of detection during transfer. WinSCP software is frequently used to orchestrate these transfers efficiently and discreetly. The scale of these operations is often considerable, with sometimes several hundred gigabytes of data extracted, potentially representing an organization’s entire information assets.
4. Deactivating defenses and deleting backups
To ensure the success of their attack, Qilin’s cybercriminals meticulously neutralize all defensive and recovery mechanisms present in the targeted system. Their approach begins with the systematic deletion of system logs, eliminating any trace of their intrusion and hampering future forensic analysis. They then strategically disable security services, such as antivirus and intrusion detection solutions, which could hinder the deployment of their ransomware.
Particular attention is paid to destroying backups and restore points. Specifically designed PowerShell commands are executed to clean Windows event logs, removing potentially crucial information for detection and investigation.
Shadow copies, Windows’ built-in backup mechanism, are also eliminated via commands such as vssadmin.exe Delete Shadows /all /quiet, depriving victims of their last resort to recover data without paying the ransom.
5. Data encryption
The encryption process deployed by Qilin demonstrates remarkable technical sophistication, designed to maximize damage while minimizing the risk of unauthorized recovery.
Attackers adapt their cryptographic approach according to the target’s technical environment. Where hardware permits, they prefer the AES-256 algorithm in CTR mode, taking advantage of hardware acceleration for fast, efficient encryption. In other cases, they fall back on ChaCha20, an algorithm renowned for its robustness and performance on systems without dedicated hardware acceleration.
To further secure their operation, critical encryption keys and parameters are themselves protected via RSA-4096 encryption, creating an additional layer of protection virtually impossible to break with current technologies.
In some particularly destructive cases, ransomware can perform multiple encryption passes on the same files, dashing any hope of recovery by conventional data recovery techniques. This encryption strategy systematically extends to local files as well as to data stored on network shares, maximizing the impact on the victim’s entire infrastructure.
6. Ransomware
After encryption, victims receive a ransom note which :
- Directs to a site on the Tor network
- Specifies the ransom amount (ranging from $25,000 to several million, depending on the size of the victim)
- Threatens to publish the exfiltrated data if the ransom is not paid
- Provides a deadline for payment (usually 5 days)
Targeted sectors and organizations
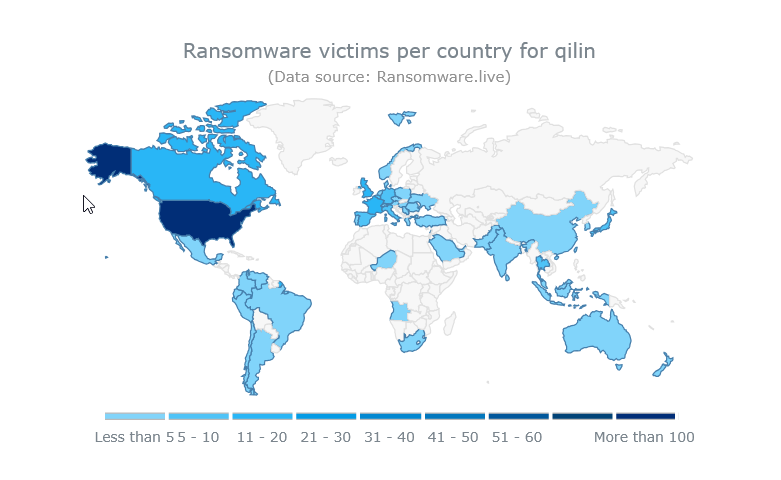
The Qilin ransomware stands out for its opportunistic and indiscriminate approach to target selection. Unlike some groups that specialize in specific sectors, Qilin affiliates seem to focus on vulnerability rather than industry, striking wherever they detect exploitable vulnerabilities.
In the healthcare sector, the attack on Synnovis in the UK had catastrophic repercussions, severely disrupting the operation of several London NHS hospitals and leading to the cancellation of hundreds of surgical operations. This case perfectly illustrates the potentially vital impact these attacks can have when they target critical infrastructures.
The media world has not been spared, as demonstrated by the attack on Lee Enterprises, a major US media group. Cybercriminals threatened to disclose 350 gigabytes of sensitive data, potentially including confidential information on journalistic sources and editorial activities.
The automotive industry also came under attack from Qilin, with the attack on Yanfeng, an automotive components giant, causing cascading disruptions affecting production at automaker Stellantis. This situation underlines the vulnerability of global supply chains to these threats.
The public sector is not to be outdone, as demonstrated by the attacks on Upper Merion Township in the USA and Australia’s Court Services Victoria. These incidents show that even government institutions and essential services are not immune.
Finally, cultural and charitable organizations have also been affected, with attacks targeting The Big Issue, a well-known UK charity, and the Houston Symphony in the USA. These cases show that even non-profit organizations can become lucrative targets for cybercriminals.
This diversity of victims underlines a worrying reality: no organization is too small or too specialized to escape Qilin’s attention. The only constant seems to be the opportunism of attackers and their ability to exploit technical and human vulnerabilities wherever they may be found.
Impact and consequences of a Qilin attack
The consequences of a Qilin ransomware attack can be devastating and multidimensional:
- Operational paralysis: Total shutdown of IT systems and business interruption.
- Loss of sensitive data: Exfiltration and potential publication of confidential data.
- Substantial financial impact: Recovery costs, business interruption and potentially ransom payments.
- Reputational damage: loss of customer and partner confidence following disclosure of an attack.
- Legal consequences: Risk of sanctions in the event of non-compliance with data protection regulations.
The most striking example is undoubtedly the attack against Synnovis in June 2024, which resulted in:
- The cancellation of over 800 operations in several London hospitals
- Major disruptions to pathology services
- A ransom demand of $50 million
- Direct impact on the health and well-being of many patients

How to protect yourself against the Qilin ransomware
To guard against the growing danger posed by Qilin, it is imperative that organizations put in place a robust and proactive multi-layered defense.
1. Access management and authentication
The first line of defense against Qilin is rigorous identity and access management. Multifactor authentication is an essential bulwark, particularly for administrative accounts and services exposed to the Internet. This simple measure can thwart many intrusion attempts, even when credentials have been compromised. Organizations should also rethink their password policies, favoring long passphrases of at least 16 characters, which are more resistant to brute-force attacks and easier to remember than complex but short combinations.
The principle of least privilege should guide the allocation of access rights, ensuring that each user has only those permissions strictly necessary to perform his or her tasks. For accounts with elevated privileges, the just-in-time (JIT) access approach offers an additional layer of protection by limiting the window of exposure of administrative rights.
2. System maintenance and updating
Technical vigilance is a fundamental pillar of any effective defense strategy against Qilin. The rapid application of security patches, particularly for known and actively exploited vulnerabilities, must be a top priority for IT teams. This discipline considerably reduces the attack surface exploitable by cybercriminals.
Antivirus solutions must be kept up to date and configured for real-time detection, offering dynamic protection against emerging threats. Network segmentation, meanwhile, limits lateral propagation in the event of an intrusion, containing potential damage to an isolated portion of the infrastructure. Finally, disabling non-essential ports and services helps reduce the number of entry points available to attackers, in line with a default security approach.
3. Monitoring and detection
To effectively counter the Qilin threat, early detection is crucial. Deploying endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions can identify and neutralize suspicious behavior before it becomes a full-blown compromise. These modern tools, often enhanced by artificial intelligence, can detect sophisticated attack patterns that traditional antivirus software might miss.
Proactive network monitoring completes the picture, identifying anomalous communications, attempted lateral movements or data exfiltration. Behavioral analysis technologies can spot unusual activities, even when they have no known signature.
To maximize the effectiveness of these solutions, secure, centralized logging is essential, ensuring that critical activity traces remain preserved, even in the event of attempted deletion by attackers.
4. Robust backup strategy
In the fight against Qilin, a carefully thought-out backup strategy is your last line of defence. Follow the tried-and-tested 3-2-1 principle: keep at least three copies of your critical data, on two different types of media, with one copy stored off-site. This redundancy ensures that even in the event of a sophisticated attack, you’ll retain access to your critical information.
It’s essential that your backups are encrypted to prevent them being exploited in the event of theft, but above all that they are designed to be immutable – i.e. protected against modification or deletion, even by users with elevated privileges. This feature is crucial, as Qilin’s operators actively target backup solutions.
Offline storage, physically disconnected from the main network, offers additional protection against ransomware, which systematically searches for and destroys accessible backups. Finally, never neglect regular restore tests, the only way to guarantee that your backups will actually work when you need them. An untested backup cannot be considered reliable in a crisis situation.
5. Training and awareness-raising
Employee training is an essential link in the defensive chain against Qilin. Cybercriminals frequently exploit human error as an initial point of entry, particularly via increasingly sophisticated phishing techniques. An effective awareness program must go beyond theoretical presentations to include practical exercises simulating real-life attacks. These simulations enable employees to recognize warning signals and acquire the appropriate reflexes in the face of phishing attempts.
Organizations must also put in place clear and accessible reporting channels, encouraging employees to report suspicious emails promptly without fear of reprimand. This culture of collective vigilance provides an invaluable early warning system.
Awareness must extend to good password management practices, discouraging their reuse between departments and promoting the use of password managers. These tools make it possible to use unique, complex identifiers for each service without compromising convenience of use.
Recovery solutions with SOS Ransomware
If, despite all precautions, your organization falls victim to the Qilin ransomware, SOS Ransomware can help you with its specialized expertise in data recovery after a ransomware attack.
Our approach to Qilin attacks
As a specialized department of Recoveo, the French leader in data recovery with over 100,000 successful rescues, we have developed a rigorous methodology for dealing with ransomware attacks, including those perpetrated by the Qilin group.
Our response begins with a rapid and accurate assessment of the attack. Our team of experts, available 24/7, meticulously analyzes the extent of the damage to determine which systems have been affected and establish clear recovery priorities. This initial step is crucial to maximize the chances of recovery while minimizing downtime for critical services.
We then proceed to isolate infected systems and create forensic copies. This careful approach ensures that no recovery action risks further compromising data or erasing potentially important evidence. Our technicians work exclusively on these copies, preserving the integrity of the original media.
Our expertise extends to all types of infrastructure, from complex servers and RAID systems to virtualized environments such as VMware, Docker, Citrix and Microsoft. We also master the recovery of data from various databases (SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, Maria DB) and backup systems (Veeam, Acronis, Arcserve), which are often the priority targets of Qilin attackers.
To accomplish these recovery missions, we use specialized tools developed in-house. These proprietary solutions enable us to intervene on the most complex systems and recover data encrypted by ransomware, even when conventional methods fail.
The final phase involves the methodical extraction of recovered data, followed by rigorous validity tests to guarantee its integrity. A detailed inventory of recovered files is then drawn up, providing clear visibility of what has been saved and enabling effective disaster recovery planning.

Why choose SOS Ransomware over Qilin?
Our expertise in dealing with ransomware has been built up through more than 250 successful interventions on similar cases. This accumulated experience has enabled us to refine our techniques and tools to respond specifically to the challenges posed by sophisticated threats like Qilin. We understand the technical peculiarities of this ransomware and have developed tailored approaches to maximize the chances of recovery.
We have devoted significant resources to developing specific tools for recovery from Veeam backup files, which are often targeted by Qilin attacks. This specialization enables us to intervene effectively even when the usual backup mechanisms have been compromised.
Speed of response is a crucial advantage in the fight against ransomware. Our emergency response team is structured to react in less than an hour, limiting the spread of damage and preserving the chances of recovery.
Don’t pay the ransom!
Giving in to the blackmail of Qilin’s cybercriminals may seem like the quickest solution, but this approach entails major risks that you must consider. Paying a ransom comes with no guarantee that your data will be recovered. Many organizations that gave in to the attackers’ demands were left with defective or incomplete decryption tools, or worse, never received the promised keys despite the transfer of funds.
Beyond the technical uncertainty, paying a ransom constitutes direct financing of criminal activities, potentially fuelling other forms of cybercrime or even terrorism. This reality explains why cybersecurity experts, including the FBI and ANSSI, formally advise against this option.
An aspect often overlooked is that paying a ransom does not eliminate the vulnerabilities that enabled the initial attack. Without full remediation, your organization remains exposed to further intrusions, potentially by the same actors who are now aware of your propensity to pay.
SOS Ransomware offers a more reliable and ethical alternative, enabling you to recover your data by legitimate means, while reinforcing your security posture to prevent future attacks.
Article source :
- Sentinelone – Agenda (Qilin) Ransomware: In-Depth Analysis
- Picus Security – Qilin Ransomware
- Wikipedia – Qilin (cybercrime group)
- Microsoft – North Korean hackers now deploying Qilin ransomware
- Darktrace – Qilin Ransomware-as-a-Service Operator
- Industrial Cyber – CISA reaffirms to safeguard US critical infrastructure
- Ransomware.live
