Cybercriminals are redoubling their ingenuity to bypass conventional protections, and the adoption of the FileFix technique by ransomware group Interlock perfectly illustrates this worrying trend. This new attack method, demonstrated by security researcher mr.d0x and operationally deployed by Interlock since July 2025, represents a notable evolution in social engineering techniques, exploiting the trust we place in the usual Windows interfaces.
Unlike traditional attacks based on software vulnerabilities, FileFix weaponizes (transforms into an offensive weapon for malicious purposes) legitimate operating system features to deceive users. This approach transforms Windows File Explorer – an everyday tool – into an infection vector, marking a turning point in cybercriminals’ initial access strategies.
Table des matières
ToggleThe anatomy of FileFix: formidable sophistication
From ClickFix foundations to FileFix innovation
The origins of the FileFix technique lie in the ClickFix method. Introduced in early 2024, this social engineering method exploits familiar Windows mechanisms to manipulate victims and deploy malicious payloads with disconcerting efficiency.
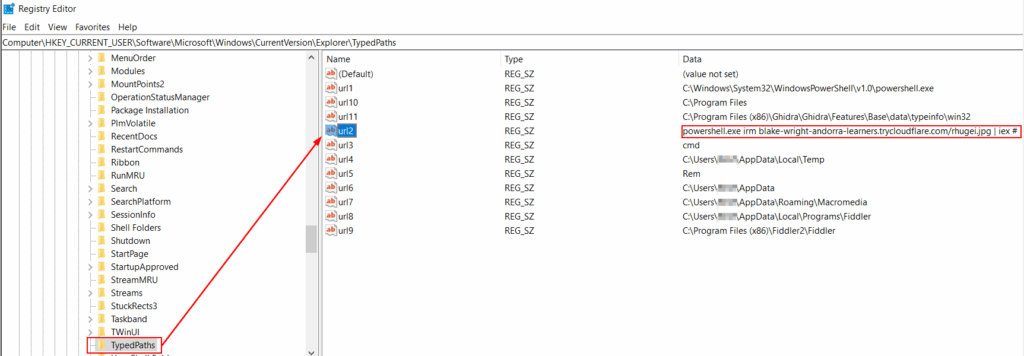
ClickFix’s fundamental principle is based on visual decoys that mimic legitimate interfaces – usually system error messages, CAPTCHA checks or bot-protection. These fake interface elements are presented to users via compromised websites, HTML attachments or phishing campaigns. When the victim interacts with these decoys by clicking on a button such as “Verify” or “Resolve”, a malicious script is automatically copied to the clipboard. Simultaneously, convincing instructions appear, guiding the user to open the Windows Run dialog (Win+R) to paste and execute the contents of the clipboard.
In September 2024, for example, Proofpoint researchers observed a campaign in German using the ClickFix technique with a fake CAPTCHA to specifically target Swiss organizations posing as the popular Ricardo marketplace.
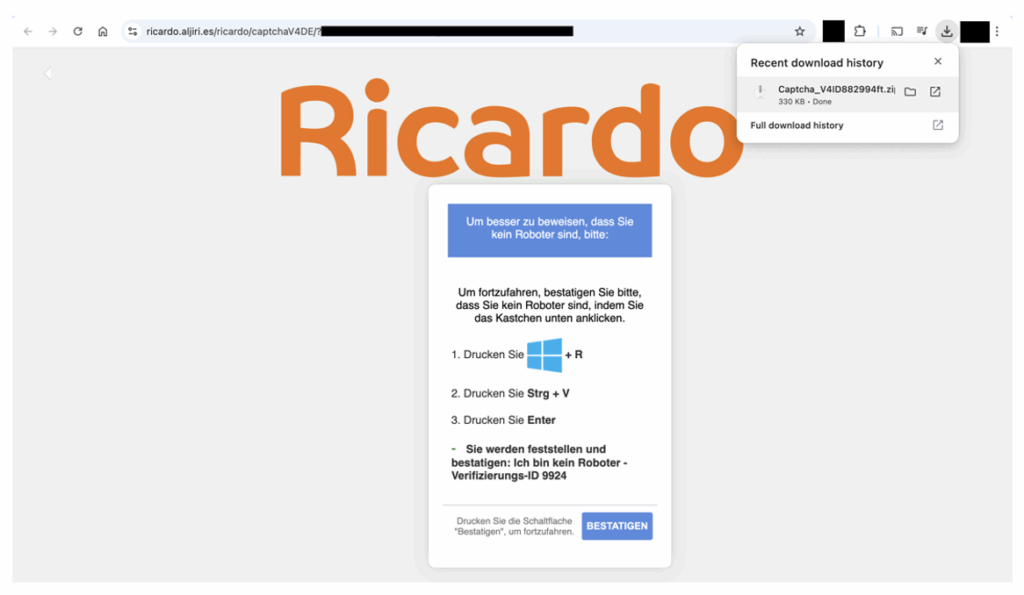
FileFix perfects this approach by moving the attack to the familiar and reassuring environment of Windows File Explorer. The original mr.d0x research, published on June 23, 2025, demonstrates how a malicious web page can simultaneously open a Windows Explorer window and silently load a disguised PowerShell command from the user’s clipboard.
Sophisticated execution mechanism
The FileFix infection process deploys a meticulously orchestrated sequence, designed according to advanced principles of behavioral psychology to increase the chances of compromise. This technique exploits our trust in the usual system interfaces, creating an experience so natural that even sophisticated users can hardly distinguish the attack from a legitimate system interaction.
In this video, John Hammond provides a detailed analysis and practical demonstration of FileFix, illustrating in concrete terms the mechanisms by which Windows Explorer is exploited and the techniques used to bypass system protections.
detailed attack sequence :
- Psychological initiation: the victim visits a compromised web page which displays a false CAPTCHA check or a convincing error message.
- Automatic opening: a JavaScript script triggers the opening of a Windows File Explorer window
- Clipboard manipulation: at the same time, the script loads a malicious PowerShell command onto the clipboard
- Misleading instructions: the user is instructed to “fix” an alleged problem by pasting the contents of the clipboard into the Explorer address bar
- Silent execution: when the user presses ‘Enter’, Windows interprets and executes the PowerShell command, triggering the infection.
Interlock’s operational adoption of FileFix
Partnership with KongTuke infrastructure
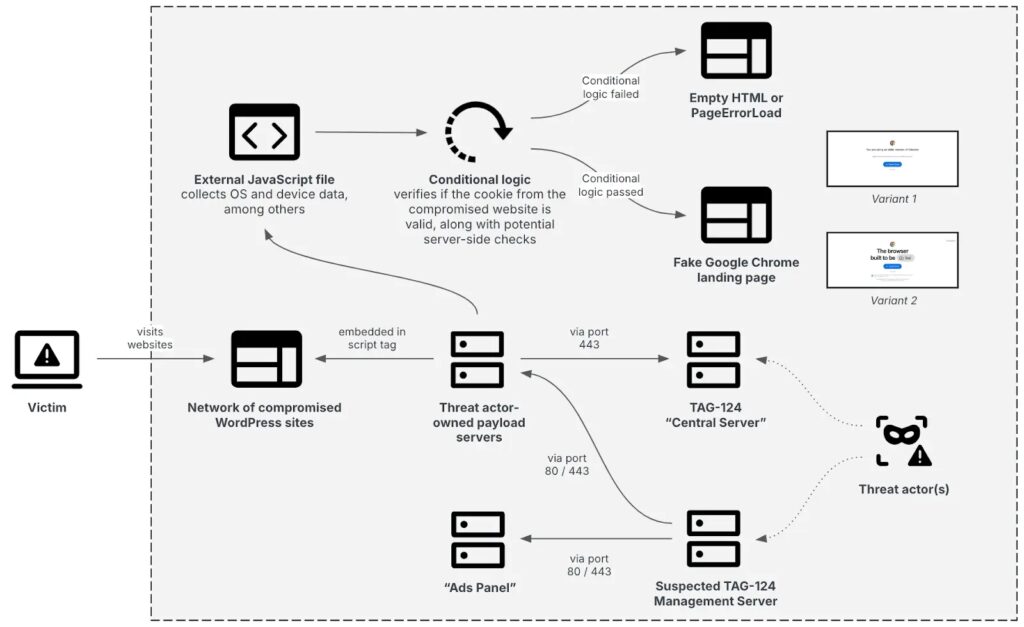
Interlock’s adoption of FileFix has not taken place in a vacuum. According to The DFIR Report’s detailed analysis, the group has established a strategic partnership with the KongTuke traffic distribution system (TDS), also known as LandUpdate808.
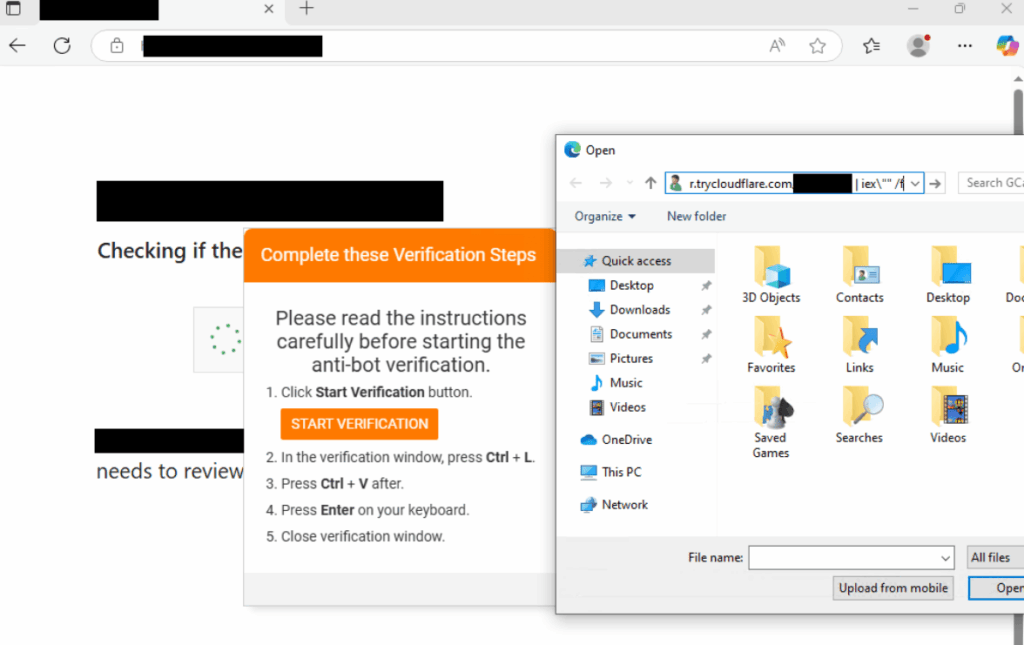
This infrastructure enables payloads to be massively distributed via compromised legitimate websites, maintain operational resilience through automatic domain rotation, avoid detection by traditional security systems and specifically target victims according to geographical and technical criteria.
Recorded Future’s research on TAG-124 reveals that KongTuke serves multiple cybercriminal groups, including Rhysida, SocGholish and now Interlock, testifying to the professionalization of criminal infrastructure services.
Evolution towards the PHP variant of the RAT (Remote Access Trojan)
Interlock’s implementation of FileFix is accompanied by a major technical evolution in their malware arsenal. Researchers from The DFIR Report and Proofpoint have identified a new PHP-based variant of the Interlock RAT, replacing previous versions using Node.js ( NodeSnake).
This migration to PHP offers several strategic advantages: increased portability, as PHP is a widely supported interpreted language, enabling the malware to run on a variety of platforms with minimal modifications. Discretion is enhanced, as the use of PHP can make detection more difficult for traditional security systems, particularly those optimized to detect classic Windows executables. Finally, maintenance is simplified as PHP scripts are easier to modify and adapt than Node.js applications, allowing malicious capabilities to evolve rapidly.
Advanced technical capabilities of Interlock’s PHP RAT
Automated recognition and system profiling
Technical analysis reveals that the new PHP variant performs immediate and exhaustive system reconnaissance as soon as it is executed. The malware automatically collects detailed system information via the systeminfo command, an inventory of running processes and services, network configuration and ARP table to identify adjacent systems, privilege level (USER, ADMIN or SYSTEM) and mapping of mounted and accessible drives.
This information gathering enables operators to immediately assess the value of the target and adapt their attack strategy accordingly.
Resilient, masked C2 infrastructure
Interlock’s PHP RAT implements a particularly robust command-and-control architecture. Cloudflare Tunnel domains enable the malware to mask the actual location of command and control servers, exploiting legitimate infrastructure to avoid detection. Backup IP addresses are integrated to ensure communications continuity even if the main tunnels are closed. Encrypted communications preserve the confidentiality of commands and data exfiltrated between the RAT and the C2 (Command and Control) infrastructure.
Extended execution capabilities
The PHP RAT’s operational capabilities are complex: download and execution of arbitrary EXE or DLL files, establishment of persistence via Windows registry keys, execution of shell commands for system administration, facilitation of lateral movement via RDP and self-destruction on command to avoid forensic analysis.
FileFix 2.0: MOTW bypass and malicious HTML applications
Evolution towards HTML Applications (.hta)
Additional research by mr.d0x, published on June 30, 2025, reveals a significant FileFix evolution exploiting HTML Applications (.hta) to bypass Windows protections. This innovative technique uses browsers’ “Save As” functionality to create executable files without triggering security alerts.
The process relies on a technical peculiarity: when an HTML page is saved via Ctrl+S with the types “Webpage, Single File” or “Webpage, Complete”, the downloaded file does not receive the Windows Mark of the Web (MOTW). This allows direct execution without security warnings.
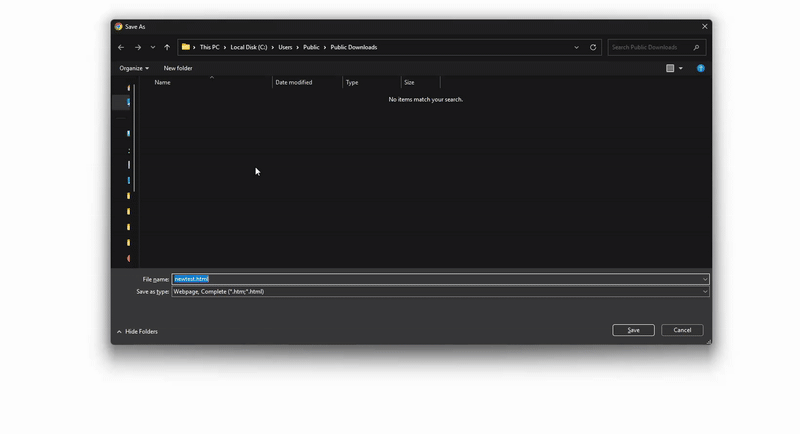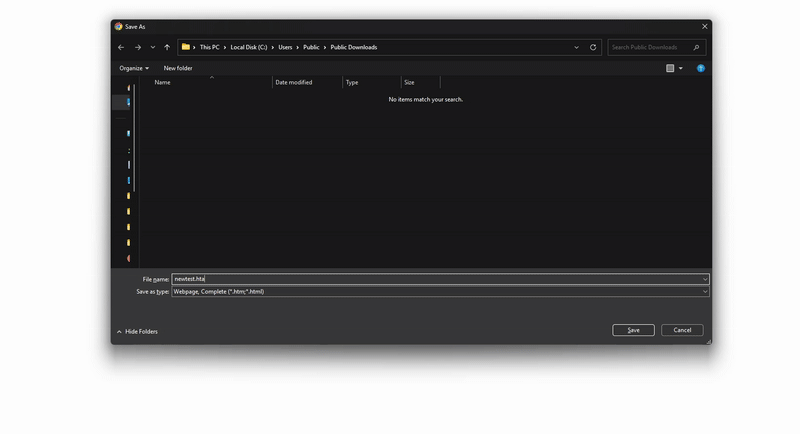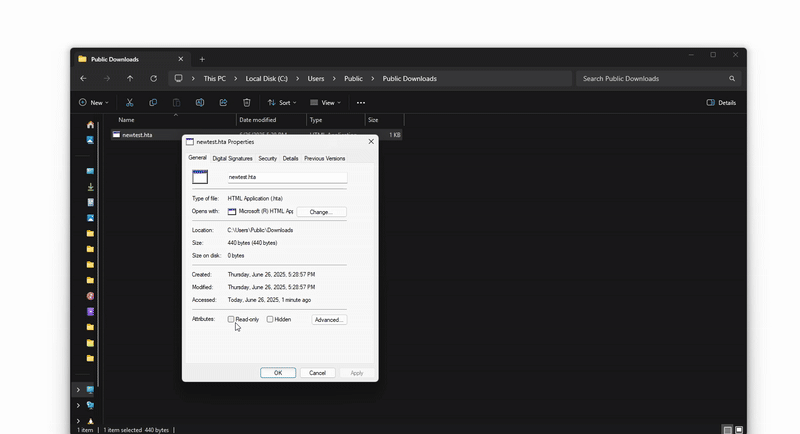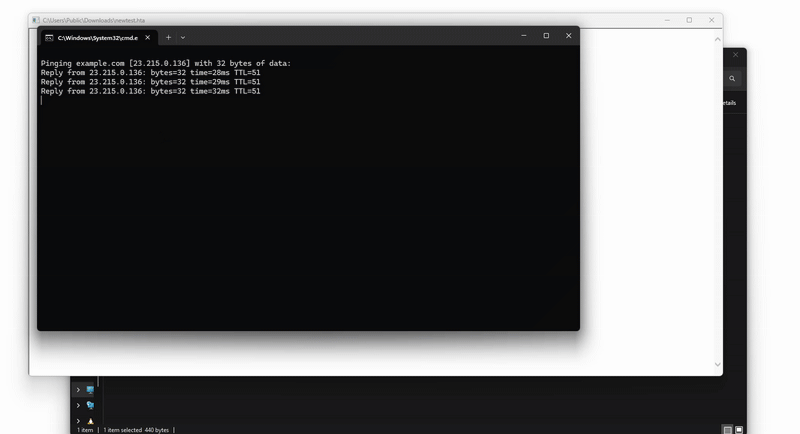
See the demo in higher quality on mr.d0x’s website
Mark of the Web bypass techniques
The MOTW bypass represents a major breakthrough in evading Windows defenses. The .hta files can process HTML content and execute JScript scripts directly, enabling system commands to be executed via ActiveX. This approach turns a simple HTML file into a stealth executable, invisible to traditional protection mechanisms.
The technique also exploits Data URIs with MIME text/html type, enabling attackers to encode the malicious payload directly in the URL and have it saved without MOTW by browsers.
New social engineering lures
FileFix 2.0 introduces particularly sophisticatedsocial engineering lures, including the saving of “recovery codes” or “backup codes” for multi-factor authentication. These lures exploit users’ familiarity with legitimate security procedures to induce them to download and execute malicious files.
The effectiveness of these new pretexts lies in their credibility: users are used to saving large recovery codes, making the download request perfectly natural.
The FileFix attack ecosystem in action
Sophisticated filtering and targeting
Analysis reveals that Interlock’s FileFix campaigns implement advanced filtering mechanisms to optimize effectiveness while reducing exposure to security systems.
Malicious code embedded in compromised sites uses advanced IP filtering to serve payloads only to targeted victims, detection of virtual environments to avoid analysis by researchers, geolocalization to adapt lures according to regions, and browser fingerprinting to personalize the attack.
Explosive growth and professionalization
The ClickFix technique, of which FileFix is the evolution, is experiencing explosive growth in the threat landscape. According to the ESET Threat Report H1 2025, ClickFix, HTML/FakeCaptcha detections increased by 517% between the second half of 2024 and the first half of 2025, confirming the massive adoption of these techniques by cybercriminals.
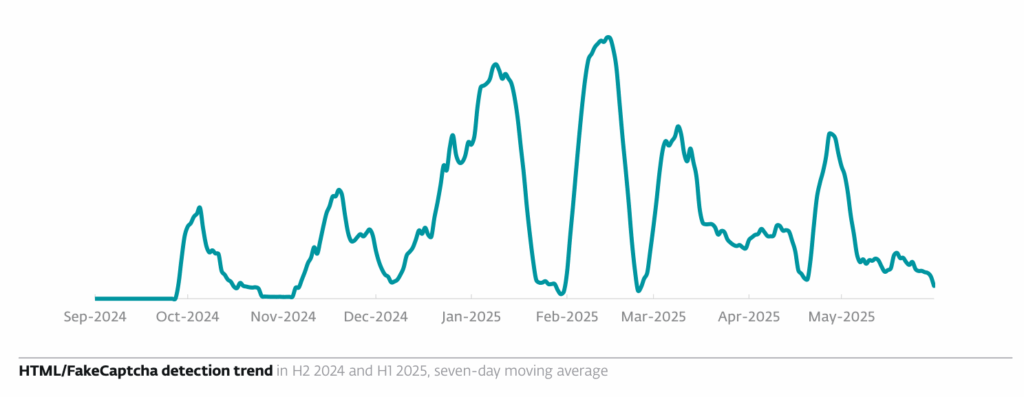
This rapid growth is explained by the proven effectiveness of these social engineering techniques, as Dušan Lacika, senior detection engineer at ESET, explains: “What makes this new social engineering technique effective is that it’s simple enough for the victim to follow the instructions, credible enough to give the impression that it could solve an invented problem, and exploits the likelihood that victims won’t pay much attention to the exact commands they’re asked to paste and execute on their device.”
Defense strategies and protective measures
Preventive technical approach
In the face of evolving FileFix techniques, organizations need to adopt a multi-layered security approach combining technical measures and human training. System configuration requires several critical adjustments: disabling automatic execution of PowerShell from File Explorer, setting up AppLocker rules to control application execution, configuring Windows Defender Application Guard to isolate browsers, and enabling detailed logging for PowerShell and scripts.
Network security also requires specific adaptations: DNS filtering to block suspicious Cloudflare Tunnel domains, monitoring traffic to known IP addresses of malicious infrastructure, network segmentation to limit lateral movements and monitoring outgoing RDP connections.
Critical training and awareness
The effectiveness of FileFix attacks relies entirely on social engineering, making user training essential. Key awareness elements include: recognizing fake CAPTCHA verification pages, distrusting instructions to paste content into File Explorer, immediately reporting suspicious website behavior and understanding the risks of executing unverified commands.
Incident detection and response
Early detection involves paying attention to a number of specific indicators: unusual execution of php.exe from user folders, connections to dubious domains such as trycloudflare.com for example, unauthorized modifications to auto-start registry keys and suspicious PowerShell activity involving downloads.
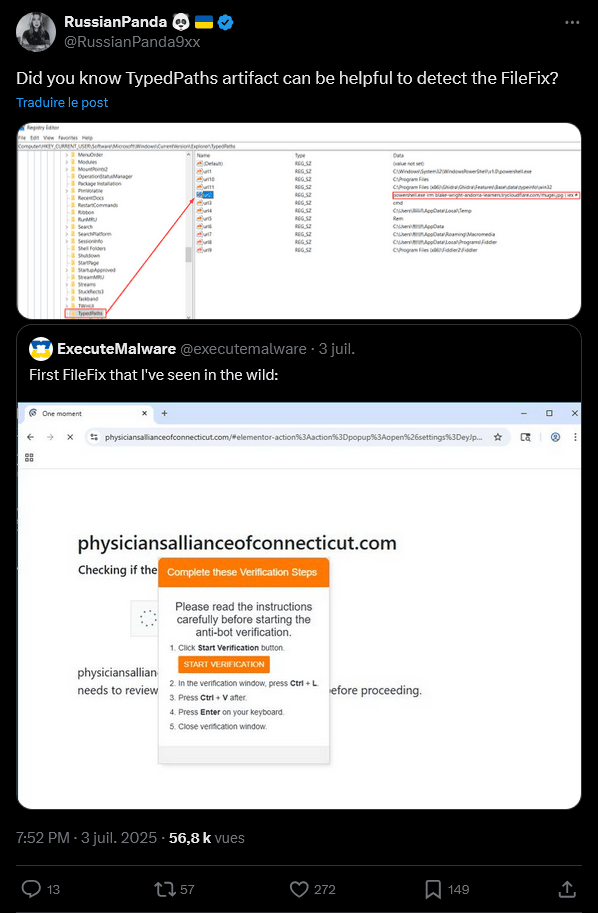
It can also be useful to monitor TypedPaths entries in the Windows registry, which automatically record paths typed in File Explorer, enabling post-incident forensic detection as RussianPanda on X noted.
FileFix: why companies urgently need to adapt
The adoption of FileFix by groups such as Interlock reveals the remarkable adaptability of cybercriminals in the face of existing defenses. This technique illustrates the ability of attackers to hijack legitimate system functionality to bypass existing protections.
Companies and organizations must now anticipate these technological changes by simultaneously strengthening their behavioral detection capabilities and their awareness programs. The challenge: stay ahead of threats that outpace traditional security updates.
Sources :
- mr.d0x: FileFix – A ClickFix Alternative
- mr.d0x: FileFix (Part 2)
- Proofpoint: Security Brief: ClickFix Social Engineering Technique Floods Threat Landscape
- Group-ib: ClickFix: The Social Engineering Technique Hackers Use to Manipulate Victims
- Sekoia: ClickFix tactic: The Phantom Meet
- The DFIR Report: KongTuke FileFix Leads to New Interlock RAT Variant
- Recorded Future: TAG-124’s Multi-Layered TDS Infrastructure
- Quorum Cyber: NodeSnake Malware Report (pdf)
- Check Point Research: FileFix: The New Social Engineering Attack Building on ClickFix
- The Hacker News: New PHP-Based Interlock RAT Variant Uses FileFix Delivery
- BleepingComputer: Interlock ransomware adopts FileFix method to deliver malware
- ESET: Threat Report H1 2025
- Department of Health and Human Services (HHS’.’gov): ClickFix Attacks Sector Alert[PDF, 707 KB]
