Toyota Financial Services (TFS), a key subsidiary of the renowned carmaker Toyota, recently faced a major cybersecurity challenge. The incident, involving unauthorized access to its systems in Europe and Africa, has raised concerns in the global automotive and financial sectors. TFS, known for its extensive automotive finance network in the markets where Toyota operates, has become the target of the Medusa ransomware group, an emerging threat in the cyber landscape.
Toyota Financial Services, a subsidiary of Toyota Motor Corporation, is a global entity present in 90% of the markets where Toyota sells its cars, and provides automotive financing services to its customers. Earlier today, the Medusa ransomware gang listed TFS on its dark web data leak site, demanding a payment of $8,000,000 to delete the data allegedly stolen from the Japanese company. Toyota Finance has not confirmed that any data was stolen in the attack, but the perpetrators of the threat claim to have exfiltrated files and threaten to leak the data if the ransom is not paid.
Table des matières
ToggleThe Medusa attack in detail
Toyota Financial Services is a subsidiary of Toyota Motor Corporation, this organization is present in 90% of the markets where Toyota sells its cars as well as providing car financing to its customers.
The Medusa ransomware group, increasingly present on the cybercrime scene, claimed responsibility for the attack. They listed TFS on their data leak blog, demanding a staggering ransom of $8 million. This demand came with a strict 10-day deadline, with an additional cost of $10,000 per day of late payment.
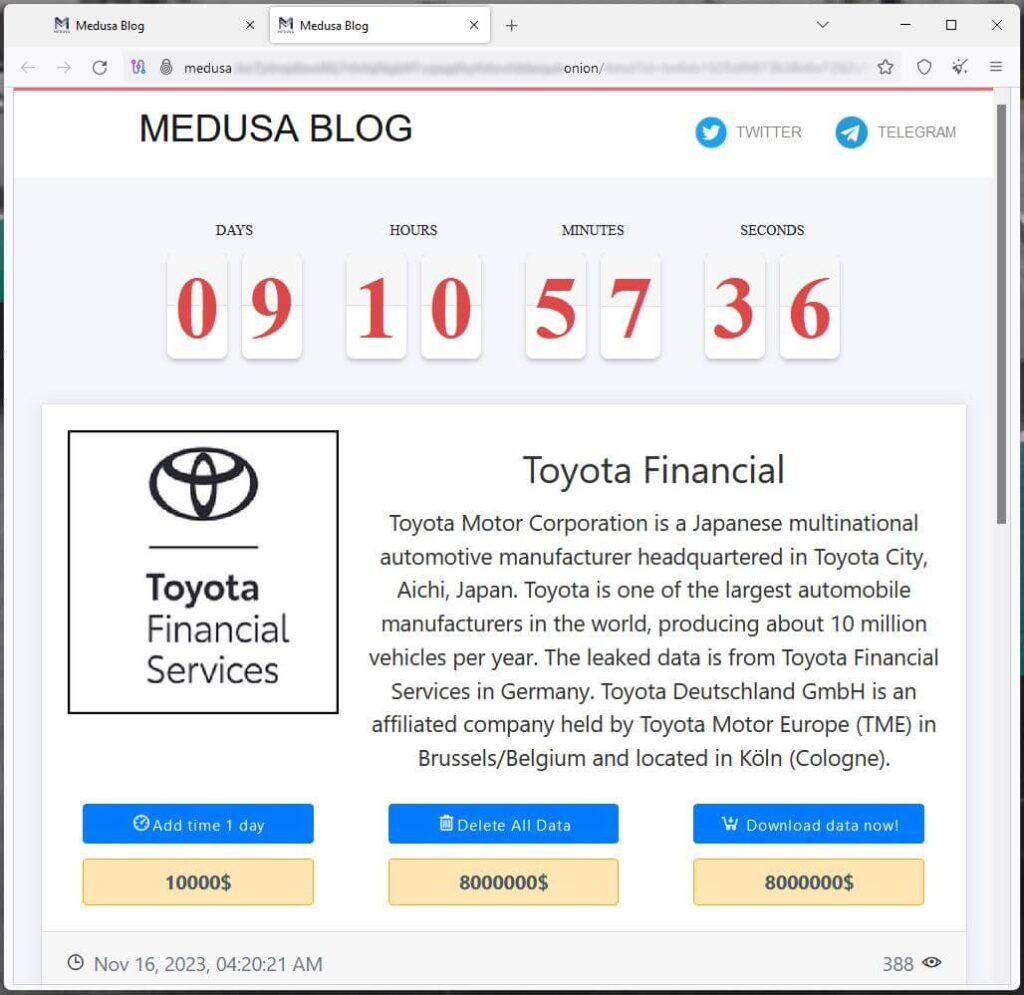
What kind of data was stolen?
The seriousness of this breach becomes clear when we consider the nature of the data involved. The hackers are said to have exfiltrated a variety of sensitive information, including:
- Financial documents and spreadsheets
- Purchase invoices
- hashed account passwords
- Unencrypted logins and passwords
- Passport scans
- Internal organization charts
- Financial performance reports
- Staff e-mail addresses
Most of these documents were in German, suggesting a significant breach in Toyota’s Central European operations.
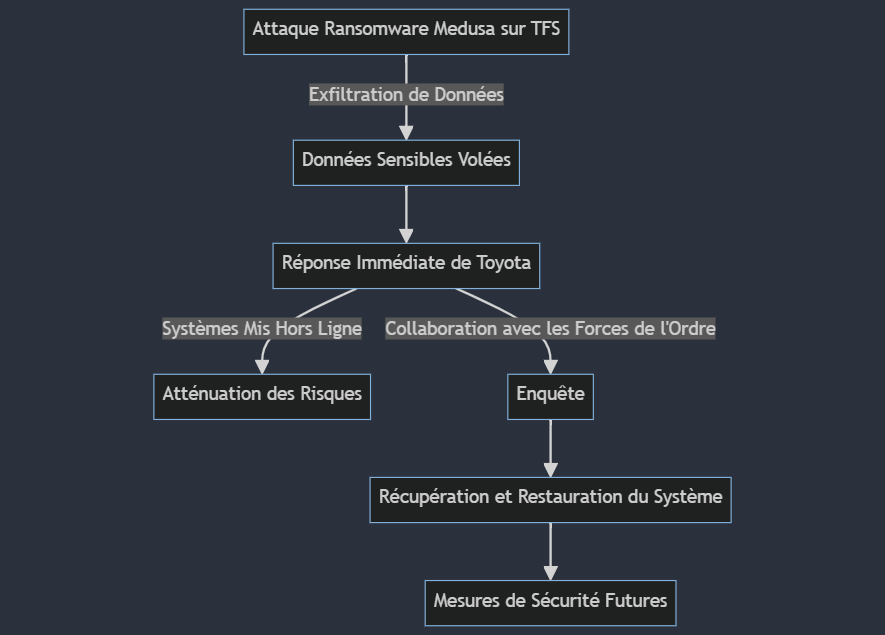
Toyota’s response and measures taken
As soon as this unauthorized access was detected, Toyota Financial Services took immediate action. Key systems were taken offline to mitigate further risks and facilitate a thorough investigation. The company also initiated collaboration with law enforcement agencies to resolve this critical issue.
Contacted by BleepingComputer a Toyota spokesperson said:
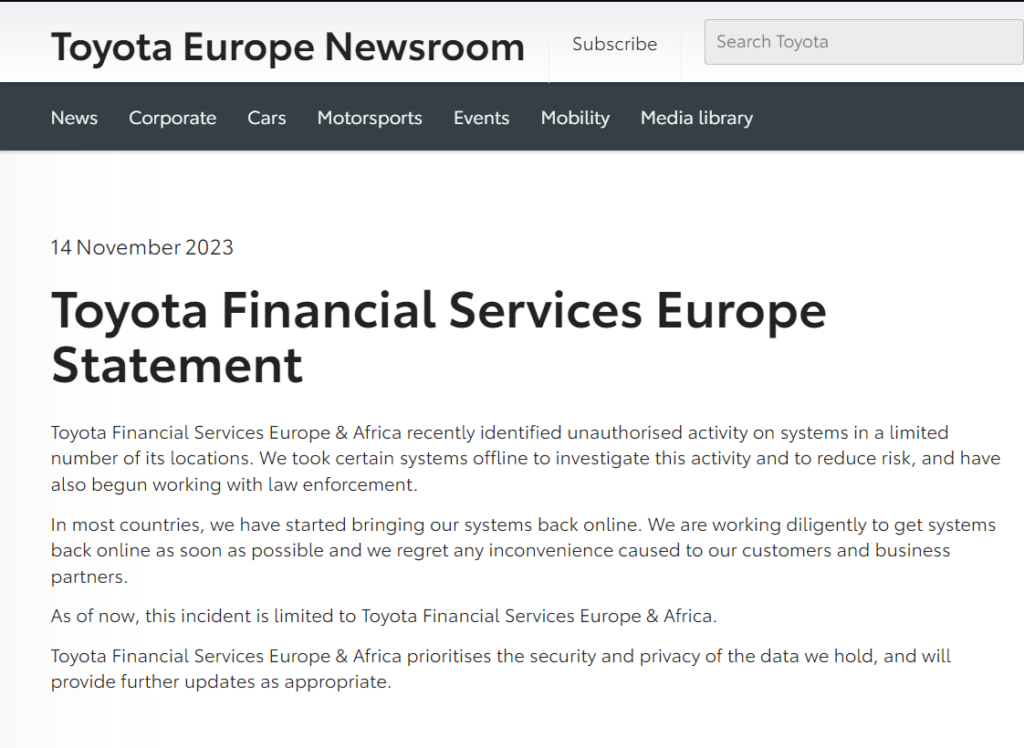
“Toyota Financial Services Europe and Africa recently identified unauthorized activity on systems at a limited number of its sites…We have taken some systems offline to investigate this activity and reduce risk, and we have also begun working with law enforcement.”
BleepingComputer
Toyota Financial Services is actively working to restore its systems. The process of bringing systems back online is already underway in most of the affected countries. This rapid response underlines Toyota’s commitment to security and its proactive approach to cyber threats.
On its website Toyota Financial Services Europe confirmed theattack on its systems in a statement:
The potential source of the vulnerabilities exploited by Medusa ransomware
The Citrix Bleed connection?
Security analysts have raised the possibility that this breach is linked to the Citrix Bleed vulnerability, as was also mentioned in the case of the Lockbit attack on Boeing. Notably, the German TFS office had an exposed Citrix Gateway endpoint on the Internet, which had not been updated since August 2023. This obsolete system could have provided an entry point for attackers.
This incident is not isolated. Other large organizations, including the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC), DP World, Allen & Overy have also fallen victim to ransomware attacks exploiting the Citrix Bleed vulnerability. The widespread nature of this vulnerability represents a significant challenge for global cybersecurity.
Lessons to be learned from this attack
The attack on Toyota Financial Services serves as a stark reminder of the evolving nature of cyber threats and the importance of robust cybersecurity measures. As ransomware groups like Medusa become more sophisticated, organizations must prioritize regular updates and patches to their security systems. Collaborative efforts between companies and law enforcement agencies are crucial to combating these threats and protecting sensitive data.
Proactive measures for future security
To prevent similar incidents, companies should:
- Regularly update and patch their cybersecurity systems
- Conduct frequent security audits and risk assessments
- Train employees in cybersecurity best practices
- Establish rapid response protocols for potential breaches
While Toyota Financial Services faces a difficult situation, their proactive and transparent approach sets a precedent for how global companies should manage and learn from cybersecurity incidents.
