Imagine ransomware that no longer encrypts your data, but terrorizes you just the same. This is the reality of Worldleaks, the criminal group revolutionizing digital extortion in 2025. By abandoning encryption in favor of pure blackmail, cybercriminals are exploiting a formidable psychological flaw: the fear of having one’s secrets exposed. Faster, more discreet and harder to detect, this new attack model overturns all the codes hitherto established in the ransomware landscape.
Table des matières
ToggleA strategic emergence in a repressive context
Worldleaks officially emerged on January 1, 2025, according to analyses by Group-IB, the first organization to publicly document this Group-IB threat. This appearance takes place in a particular context, where the operators of Hunters International had announced in November 2024 the discontinuation of their initial project, deeming the ransomware sector “too risky and unprofitable” due to government actions and the global geopolitical impact.
The group justified this transition by the need to adapt to the new constraints of the criminal market: ransomware payments dropped by 35% in 2024 according to a Chainalysis report, while paradoxically, unencrypted extortion attacks saw their payments increase by 41% in the fourth quarter of 2024 according to Coveware.
The Hunters International legacy: from Hive to Worldleaks
Hunters International, the predecessor of Worldleaks, was itself suspected of being a rebranding of the Hive group, dismantled by law enforcement in early 2023. This technical filiation can be seen in the similarities in code and infrastructure between the different iterations of the group.
Worldleaks’ operators have retained the sophisticated technical architecture developed by Hunters International, notably a tool similar to Hunters International’s Storage Software, enabling them to manage the metadata of exfiltrated files without storing them directly on the group’s servers. This approach has the advantage of reducing the risk of exposure for operators, while maintaining control over stolen data.
A revolutionary operational model: extortion without encryption
The “single extortion” philosophy
Unlike traditional ransomware, which encrypts AND steals data, Worldleaks focuses exclusively on exfiltration and the threat of publication. This approach, dubbed“single extortion” or“extortion-only“, offers several strategic advantages for cybercriminals:
- Reduced technical traces: the absence of encryption limits the number of artifacts detectable by security solutions.
- Faster operations: attackers can exfiltrate and threaten more quickly without the encryption phase.
- Reduced legal risks: some jurisdictions treat extortion and computer sabotage differently.
Four-tier infrastructure
Worldleaks deploys a sophisticated technical architecture comprising four distinct platforms:
1. The main leak site: public showcase of the victims and countdown to publication of the data
2. The negotiation panel: secure interface for victims to communicate with criminals
3. The Insider platform: privileged access for journalists with a 24-hour lead on leaks
4. Affiliate panel: management tool for affiliated cybercriminals
Analysis of victims and targeted sectors
Geography and industries affected
Since its launch, Worldleaks has claimed 62 victims according to Ransomware.live data as of August 19, 2025. The geographical breakdown shows a concentration on :
- 50% of victims in the USA
- Significant presence in Canada and Europe
- A few cases in Asia, despite announced restrictions
The sectors most affected reflect an opportunistic strategy:
- Healthcare: 12 victims (19.7%)
- Technology: 9 victims (14.8%)
- Manufacturing: 8 victims (13.1%)
- Energy: 4 victims (6.6%)
Emblematic victims
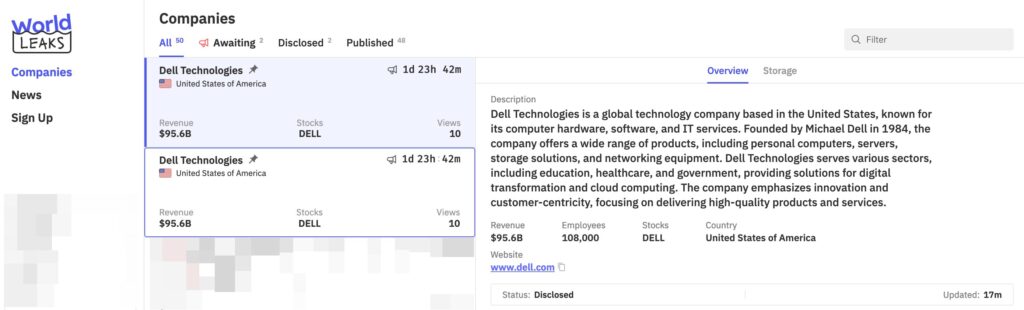
Dell Technologies was one of the most high-profile victims, with 1.3TB of stolen data and 416,103 files published in July 2025. Dell downplayed the impact, describing the data as “mainly synthetic”.
L3Harris Technologies, a US defense contractor involved in the Golden Dome missile defense system, was also targeted, demonstrating the group’s ability to attack critical infrastructures.
Techniques, tactics and procedures (TTPs)
Initial access methods
Analysis of incidents attributed to Worldleaks reveals several preferred intrusion vectors:
- Targeted phishing with malicious attachments (T1566.001)
- Exploitation of applications exposed on the Internet (T1190)
- Compromise of insecureVPNs without multi-factor authentication
- Use of compromisedvalid accounts (T1078.002)
Progression through the system
Once initial access has been gained, the group deploys a proven methodology:
Recognition and escalation of privileges:
- Information gathering via PowerShell (T1059.001)
- Exploitation of vulnerable drivers (BYOVD – T1068)
- Clearing credentials from LSASS memory (T1003.001)
Lateral movement:
- Use of RDP protocol with stolen credentials (T1021.001)
- Exploitation of SMB and WMI shares
- Discovery of network shares (T1135)
Exfiltration:
- Using tools such as Rclone, Mega.io or FTP (T1567)
- Customized storage software to catalog and organize stolen data
Specialized technical tools
The Storage Software represents Worldleaks’ major technical innovation. This tool, compatible with Windows and Linux (x86, x64), enables you to :
- index the metadata of exfiltrated files without uploading them
- Bridge the gap between criminal-controlled servers and management panels
- Use SOCKSv5 connections via Tor to secure communications
- Provide victims with direct access to download and delete their own data
Indicators of compromise (IOCs)
Technical signatures
File hashes:
- 6a9c0f3f2c7d9e9fd2e33e71b91d5e5f6cbd27ef
- e4c1a3e345a2f5d872ea04cd1fd3a7725b927ffa
Command and control infrastructure:
- 185.217.69.101
- worldleaksbackup[.]onion
- filesharevault[.]net
File extensions: .worldleaks (when encryption is used)
Registry changes: HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRunwldboot
Specific Onion addresses
According to Lexfo Security’s analysis, Worldleaks uses several distinct Tor services:
- worldleaksartrjm3c6vasllvgacbi5u3mgzkluehrzhk2jz4taufuid[.]onion (main site)
- vw6vklsuotptwdbiwqfvd7y4b57wdbfm6ypxduzzgbt62snti6jm76yd[.]onion (victim panel)
- 3jguvp6xhyypdjgxhxweu4zklse66v3awjj2zljpftcjyeoimepnwtyd[.]onion (Insider platform)
Defense and mitigation strategies
Essential preventive measures
Access management and authentication:
- Mandatory implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) on all remote access points, especially VPN and RDP
- Regular privilege audits and application of the principle of least privilege
- Strict network segmentation to limit lateral movements
Secure communications:
- Advanced e-mail filtering with anti-phishing behavioral analysis
- Monitoring of externaldata transfers, particularly to cloud services
- Detection of Tor connections and other anonymizing proxies
Detection and response
Behavioral monitoring:
- Monitoring of PowerShell scripts and detection of Cobalt Strike beacons
- Analysis of abnormal access to network shares and databases
- Event correlation via SIEM to identify exfiltration patterns
Specific detection rules:
- Unusual use of tools such as Rclone to external cloud services
- Repeated access to multiple network shares in a short space of time
- RDP connections from unusual geolocations
Protection of critical data
Enhanced backup strategy to guard against the risk of damaged backups:
- Immutable offline backups with regular restore tests
- Encrypted backups with secure key management
- Tested and documentedbusiness continuity plans
The criminal ecosystem: affiliations and collaborations
The “Extortion-as-a-Service” (EaaS) model
Worldleaks operates on an affiliation model where independent cybercriminals use the group’s tools and infrastructure in exchange for a percentage of the profits. This approach offers several advantages:
- Scalability of operations without direct expansion of the core team
- Dilution of legal and operationalrisks
- Specialization of roles between tool developers and field operators
Collaboration with Secp0
Lexfo Security’s analysis reveals a confirmed collaboration with the Secp0 group, which continues to use traditional ransomware while publishing its victims via the Worldleaks platform. This hybridization shows the growing attractiveness of the model for other malicious actors.
Economic impact and market trends
Payment trends
Payment statistics reveal a transformation of the criminal market. While traditional ransomware payments are falling, pure extortion attacks are seeing their success rates rise. This trend can be explained by several factors:
- Psychological pressure maintained without the technical complications of decryption
- More flexible negotiations without the constraints of decryption keys
- Legal risks perceived as lower by some organizations
Average cost of incidents
According to our analyses at SOS Ransomware, the cost of recovering from a Worldleaks attack is generally 2 to 10 times less than the amount of the ransom demanded. This significant saving justifies the use of specialized recovery services rather than paying the criminals directly.
Technical challenges for recovery
Specificities of extortion without encryption
The absence of encryption does not mean the absence of damage. Worldleaks victims face particular challenges:
System corruption: even without encryption, intrusions often cause collateral damage to infrastructures
Prolonged compromise: exfiltration requires prolonged access, multiplying the risk of persistent backdoors.
Contamination of backups: backups may be corrupted or contain malware during the period of infiltration.
Specialized recovery solutions
At SOS Ransomware, we have developed specific data recovery methodologies to deal with Worldleaks incidents:
- Selective restoration from pre-intrusion backups
- Reconstruction of databases from uncompromised fragments
- File recovery using our proprietary forensic tools
- Research into specific solutionsto emerging threats
Forecast and evolution of the Worldleaks ransomware
Trends in the first half of 2025
A Sophos report published in June 2025 confirms the emergence of a new criminal strategy focusing on theft and the threat of data publication without system encryption. Cybercriminals are adapting their methods in the face of better-prepared organizations capable of restoring data from backups. This trend could accelerate if it proves more profitable and less risky for cybercriminals.
Expansion risks
Several factors suggest a potential expansion of the Worldleaks model:
- Operational simplicity, attracting new, less technical players
- Reduced barriers to entry thanks to the affiliation model
- Adaptation to growingregulatory pressure on traditional ransomware
Impact on the security ecosystem
This evolution is forcing an adaptation of defensive strategies:
- Reinforcement of exfiltration monitoring to the detriment of encryption detection alone
- Evolution of cyber insurance to cover new forms of extortion
- Adapting regulations to deal specifically with extortion through data theft.
Strategic recommendations
For organizations
Risk assessment:
- Complete audit of sensitive data and classification by criticality level
- Mapping of privileged accesses and exposure areas
- Assessment of backup processes and their resistance to prolonged intrusions
Defensive reinforcement:
- Deployment of advanced EDRs with behavioral detection
- Setting up honeypots to detect lateral movements
- Specialized training of SOC teams in new extortion TTPs
For incident response
In the event of a confirmed Worldleaks incident:
- Immediate isolation of suspected systems without extinction (preservation of evidence)
- Contact with SOS Ransomware to assess the extent of the compromise
- Full documentation of early indicators of compromise
- Preservation of logs and forensic artifacts before they are corrupted
Avoid critical errors:
- Never restore backups directly without prior analysis
- Never reformat servers before extracting evidence
- Never negotiate directly with criminals without legal expertise
Conclusion: towards a new era of cyberthreats
Worldleaks represents more than just a technical evolution: it’s a paradigm shift in the digital criminal economy. The shift from encryption to pure extortion marks a strategic adaptation to the new constraints of the criminal market and the pressures exerted by the authorities.
This evolution poses unprecedented challenges for cybersecurity: how can we detect and counter attacks that do not leave the traditional traces of encryption? How can we adapt our defensive strategies to threats that are stealthier but just as devastating?
SOS Ransomware’s expertise is constantly adapting to these new realities. Our teams are constantly developing new tools and methodologies to deal with these new types of incidents, and our 20 years’ experience in the sector means we can anticipate and respond effectively to changes in the threat.
In the face of Worldleaks and similar groups, prevention remains the best defense, but when the incident occurs, specialized expertise becomes indispensable. The stakes are no longer limited to the technical recovery of data: they encompass crisis management, communication, and the complete rebuilding of digital trust.
The future of cybersecurity today lies in our collective ability to understand, anticipate and neutralize these new forms of digital crime. Worldleaks is just the beginning of a deeper transformation of the threat landscape, and only a proactive and expert approach will enable us to meet the challenges ahead.
Contact SOS Ransomware now for a free assessment in the event of an attack by the worldleaks ransomware. Our experts are available 24/7.
Main article sources :
- Group-IB: The beginning of the end: the story of Hunters International
- Lexfo: World Leaks: An Extortion Platform
- Ransomware live: Worldleaks group
